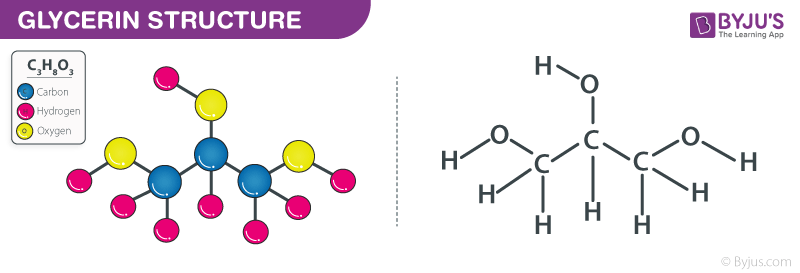
Glycerin, also known as glycerol, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C3H8O3. Some important properties and applications of glycerin are provided in this article.
What is Glycerol?
Glycerol is a non-toxic, colourless, viscous, and a simple triol compound. Glycerin or glycerol has several benefits and is mostly used in dermatological treatments and in the food industry as a preservative and sweetener. The chemical Glycerol Formula is C3H8O3. The glycerol molecule is made up of three carbon chains, each with three hydroxyl groups (OH). Since the carbon atoms are arranged in an sp3 arrangement, the molecule rotates freely.
Glycerol is water soluble and hygroscopic. It’s an essential lipid with a backbone that can be found in all triglycerides. Its applications include pharmaceuticals, the food industry, and cosmetics (like soaps).
What are the Properties of Glycerin?
The essence of glycerin is that it is hygroscopic. It can be present in lipids such as triglycerides and comes from both animal and plant sources. The three hydroxyl groups in glycerin make it water soluble.
Glycerin is a colourless, viscous liquid. Glycerin is non-toxic, odourless, and sweet in flavour. It’s often used as a sweetener, solvent, medicinal ingredient, or emollient. It is soluble in water. Triglycerides are saponified, hydrolyzed, and transesterified to create glycerin. Propylene can be used to make synthetic glycerol. Under standard conditions for temperature and pressure (often abbreviated to STP), glycerin is known to exist in the form of a colourless hygroscopic liquid that does not have any characteristic odour. This compound is known to form miscible mixtures with water.
What are the Uses of Glycerin?
Glycerin’s main use is in the food and beverage industry, where it is used as a humectant, sweetener, and solvent. Glycerin can also be used as a preservative in food storage. The following are some of the most significant applications for glycerin.
- Glycerin is a sweetener and preservative used in the food industry.
- It’s also used as a thickening agent in liqueurs.
- Glycerin is sometimes used as a filler in low-fat food products such as cookies.
- Glycerin is also used as a lubricant and humectant in the medicinal and pharmaceutical industries.
- Glycerin is a drug that is used to treat very high eye pressure.
- Glycerin is used in many skin-care items to help avoid dry skin because of its moisturising properties.
- C3H8O3 is a chemical compound that is used in the pharmaceutical industry to make cough syrups.
- Many skincare products contain glycerin as a key ingredient. This substance is also used in the manufacture of toothpaste.
- Another important use of glycerin is in the manufacture of electronic cigarette liquid.
- It’s used in dynamite and other explosives.
- C3H8O3 is used as a filler in pressure gauges to reduce vibrations.
- Glycerin is used in the film industry to prevent damp areas from drying too quickly.
Thus, some important glycerin uses were provided in this article along with its chemical formula and its properties. It is important to note that glycerin is moderately antimicrobial and antiviral and can therefore be used for wound treatment.