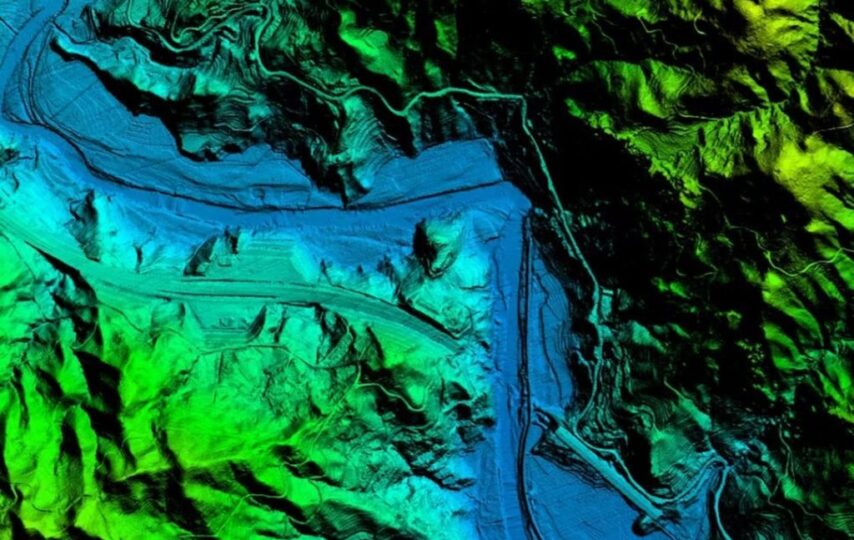
In the vast realm of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) stand as a cornerstone, revolutionizing how we understand and analyze the Earth’s topography. In this blog post, we’ll embark on a journey into the world of DEM in GIS, unraveling its definition, applications, and the transformative impact it has on various fields.
Defining DEM in GIS:
A Digital Elevation Model (DEM) is a digital representation of the Earth’s surface topography, capturing the elevation values of terrain features in a gridded format. This structured data allows GIS professionals, researchers, and environmental analysts to visualize, model, and analyze the landscape in three dimensions.
Key Components of DEM:
- Grid of Elevation Values:
- DEMs consist of a grid where each cell or pixel holds a numerical value representing the elevation of the corresponding location on the Earth’s surface.
- Spatial Resolution:
- Spatial resolution refers to the size of each pixel in the DEM grid. Higher resolution DEMs provide more detailed elevation information but may require more storage and processing power.
- Accuracy and Precision:
- The accuracy and precision of a DEM are crucial factors. Accurate elevation data is essential for applications such as hydrological modeling, slope analysis, and landform classification.
Applications of DEM in GIS:
- Terrain Analysis:
- DEMs enable in-depth terrain analysis, allowing GIS professionals to identify landforms, slopes, and elevation patterns.
- Slope analysis is crucial for assessing the suitability of areas for construction, agriculture, or other land use planning.
- Hydrological Modeling:
- DEMs play a pivotal role in hydrological modeling by delineating watersheds, identifying flow directions, and mapping the drainage network.
- The data aids in understanding surface water flow, contributing to effective water resource management.
- Viewshed Analysis:
- Viewshed analysis utilizes DEMs to determine the areas visible from specific viewpoints.
- This is valuable in urban planning, telecommunications, and environmental studies to assess visual impacts and line-of-sight considerations.
- 3D Visualization:
- DEMs bring landscapes to life in three dimensions, facilitating immersive 3D visualizations.
- This capability is used in fields such as urban planning, environmental impact assessment, and tourism.
- Natural Resource Management:
- DEMs assist in monitoring and managing natural resources by providing information on elevation variations, land cover, and land use.
- Forest management, soil erosion modeling, and ecological studies benefit from DEM data.
Conclusion:
In the dynamic world of GIS, Digital Elevation Models stand as a powerful tool, offering a wealth of information about the Earth’s surface. From terrain analysis to hydrological modeling, DEMs contribute significantly to decision-making processes across various industries. As technology advances, the precision and accessibility of DEM data continue to improve, paving the way for even more sophisticated and insightful applications in the realm of Geographic Information Systems.